|
|
马上注册,结交更多好友,享用更多功能^_^
您需要 登录 才可以下载或查看,没有账号?立即注册
x
课件代码中的一处不明白的,
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <ctype.h>
- #include <stdlib.h>
- #define STACK_INIT_SIZE 20
- #define STACKINCREMENT 10
- #define MAXBUFFER 10
- typedef double ElemType;
- typedef struct
- {
- ElemType *base;
- ElemType *top;
- int stackSize;
- }sqStack;
- InitStack(sqStack *s)
- {
- s->base = (ElemType *)malloc(STACK_INIT_SIZE * sizeof(ElemType));
- if( !s->base )
- exit(0);
- s->top = s->base;
- s->stackSize = STACK_INIT_SIZE;
- }
- Push(sqStack *s, ElemType e)
- {
- // 栈满,追加空间,鱼油必须懂!
- if( s->top - s->base >= s->stackSize )
- {
- s->base = (ElemType *)realloc(s->base, (s->stackSize + STACKINCREMENT) * sizeof(ElemType));
- if( !s->base )
- exit(0);
- s->top = s->base + s->stackSize;
- s->stackSize = s->stackSize + STACKINCREMENT;
- }
- *(s->top) = e; // 存放数据
- s->top++;
- }
- Pop(sqStack *s, ElemType *e)
- {
- if( s->top == s->base )
- return;
- *e = *--(s->top); // 将栈顶元素弹出并修改栈顶指针
- }
- int StackLen(sqStack s)
- {
- return (s.top - s.base);
- }
- int main()
- {
- sqStack s;
- char c;
- double d, e;
- char str[MAXBUFFER];
- int i = 0;
- InitStack( &s );
- printf("请按逆波兰表达式输入待计算数据,数据与运算符之间用空格隔开,以#作为结束标志: \n");
- scanf("%c", &c);
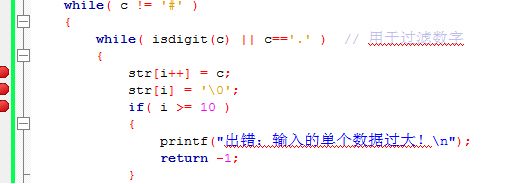
- while( c != '#' )
- {
- while( isdigit(c) || c=='.' ) // 用于过滤数字
- {
- str[i++] = c;
- str[i] = '\0';
- if( i >= 10 )
- {
- printf("出错:输入的单个数据过大!\n");
- return -1;
- }
- scanf("%c", &c);
- if( c == ' ' )
- {
- d = atof(str);
- Push(&s, d);
- i = 0;
- break;
- }
- }
- switch( c )
- {
- case '+':
- Pop(&s, &e);
- Pop(&s, &d);
- Push(&s, d+e);
- break;
- case '-':
- Pop(&s, &e);
- Pop(&s, &d);
- Push(&s, d-e);
- break;
- case '*':
- Pop(&s, &e);
- Pop(&s, &d);
- Push(&s, d*e);
- break;
- case '/':
- Pop(&s, &e);
- Pop(&s, &d);
- if( e != 0 )
- {
- Push(&s, d/e);
- }
- else
- {
- printf("\n出错:除数为零!\n");
- return -1;
- }
- break;
- }
- scanf("%c", &c);
- }
- Pop(&s, &d);
- printf("\n最终的计算结果为:%f\n", d);
- return 0;
- }
在筛选数字和小数点的代码中为什么要用str[i]='\0'?
|
-
|
 ( 粤ICP备18085999号-1 | 粤公网安备 44051102000585号)
( 粤ICP备18085999号-1 | 粤公网安备 44051102000585号)