|
|
马上注册,结交更多好友,享用更多功能^_^
您需要 登录 才可以下载或查看,没有账号?立即注册
x
- Given a linked list, determine if it has a cycle in it.
- To represent a cycle in the given linked list, we use an integer pos which represents the position (0-indexed) in the linked list where tail connects to. If pos is -1, then there is no cycle in the linked list.
-
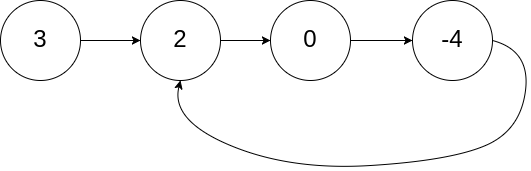
- Example 1:
- Input: head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
- Output: true
- Explanation: There is a cycle in the linked list, where tail connects to the second node.
-
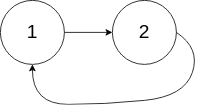
- Example 2:
- Input: head = [1,2], pos = 0
- Output: true
- Explanation: There is a cycle in the linked list, where tail connects to the first node.
-

- Example 3:
- Input: head = [1], pos = -1
- Output: false
- Explanation: There is no cycle in the linked list.
- Follow up:
- Can you solve it using O(1) (i.e. constant) memory?
- /**
- * Definition for singly-linked list.
- * class ListNode {
- * int val;
- * ListNode next;
- * ListNode(int x) {
- * val = x;
- * next = null;
- * }
- * }
- */
- public class Solution {
- public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
- if(head == null || head.next == null) return false;
- ListNode slow = head;
- ListNode fast = head;
-
- slow = slow.next;
-
- if(fast.next.next != null)
- fast = fast.next.next;
- else
- return false;
-
- while(fast != slow){
-
- if(fast == null) return false;
-
- slow = slow.next;
- if(fast.next == null) return false;
- if(fast.next.next == null) return false;
- fast = fast.next.next;
- }
-
- return true;
-
- }
- }
|
|
 ( 粤ICP备18085999号-1 | 粤公网安备 44051102000585号)
( 粤ICP备18085999号-1 | 粤公网安备 44051102000585号)