|
|
马上注册,结交更多好友,享用更多功能^_^
您需要 登录 才可以下载或查看,没有账号?立即注册
x
- #include <stdio.h>
- int main()
- {
- int array[9] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9};
- int (*p)[3] = (int (*)[3])&array;
- printf("%d\n", p[2][2]);
- return 0;
- }
- int (*p)[3] = (int (*)[3])&array;
这个代码等号的右边怎么将 array 这个一位数组重新划分成 3 * 3 的二维数组的?有点理解不了,求解!
在C语言中,数组是顺序排列,数组名实际上就是一个地址,使用数组的初始地址是可以改变行列长度的,甚至还可以改变维度。
给你举个例子:
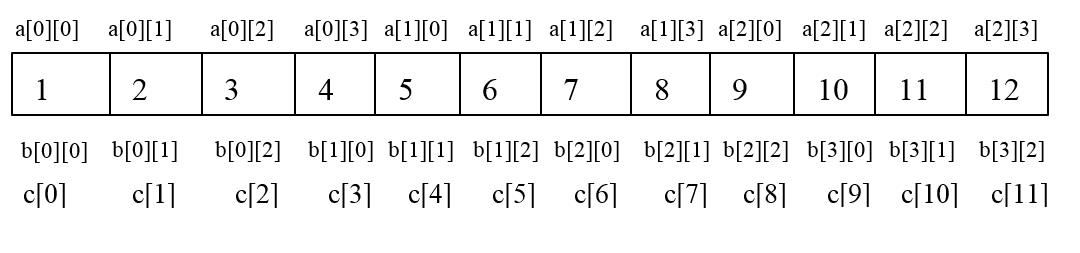
- #include <stdio.h>
- void func(int b[][3]);
- void func1(int c[])
- {
- printf("c[8]=%d\n", c[8]);
- }
- void func(int b[][3])
- {
- printf("b[2][2]=%d\n", b[2][2]);
- }
- int main(void)
- {
- int a[3][4] = {
- {1, 2, 3, 4},
- {5, 6, 7, 8},
- {9, 10, 11, 12}
- };
- func(a);
- func1(a);
- return 0;
- }
运行结果:
|
|
 ( 粤ICP备18085999号-1 | 粤公网安备 44051102000585号)
( 粤ICP备18085999号-1 | 粤公网安备 44051102000585号)