|
|
20鱼币
本帖最后由 巴巴鲁 于 2020-8-21 21:38 编辑
- /*
- 1 代表海岸线,0 代表小岛。求小岛面积(即被 1 中包围的 0 的个数)。
- 注意:仅求这样的 0,该 0 所在行中被两个 1 包围,该 0 所在列中被两个
- */
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <stdlib.h>
- #define N 6 // 假设是6维的方阵
- void input(int (*arr)[N]);
- int check(int (*arr)[N], int row, int col);
- int main(void)
- {
- int i, j;
- int count = 0;
- int arr[N][N] = {0};
-
- input(arr);
-
- // 由题意知,小岛在矩阵边缘不属于小岛面积
- for(i = 1; i < N-1; i++)
- {
- for(j = 1; j < N-1; j++)
- {
- // 只判断是小岛周围
- if(arr[i][j] == 0)
- {
- if(check(arr, i, j)) // 如果检查后满足条件,小岛面积加1
- {
- count++;
- }
- }
- }
- }
-
- printf("小岛面积为%d\n",count);
- system("pause");
- return 0;
- }
- void input(int (*arr)[N])
- {
- int i, j;
-
- for(i = 0; i < N; i++)
- {
- for(j = 0; j < N; j++)
- {
- scanf("%d",&arr[i][j]); // 只能输入0或1
- if(arr[i][j] != 0 && arr[i][j] != 1)
- {
- printf("输入错误,退出程序");
- exit(1);
- }
- }
- }
- }
- // 判断是否符合题目要求
- int check(int (*arr)[N], int row, int col)
- {
- int h, l, m, n;
- m = n = 0;
-
- // 检查行
- for(h = row, l = col; l >= 0; l--)
- {
- if(arr[h][l] == 1)
- {
- for(h = row, l = col; l < N; l++)
- {
- if(arr[h][l] == 1)
- {
- n++; // 都满足,n+1
- break;
- }
- }
- if(n == 1)
- {
- break;
- }
- }
- }
-
- // 检查列
- for(h = row, l = col; h >= 0; h--)
- {
- if(arr[h][l] == 1)
-
- for(h = row, l = col; h < N; h++)
- {
- if(arr[h][l] == 1)
- {
- m++; // 都满足,m+1
- break;
- }
- }
- if(m == 1)
- {
- break;
- }
- }
-
- if(m + n == 2) // 两个条件都成立
- {
- return 1;
- }
- return 0;
- }
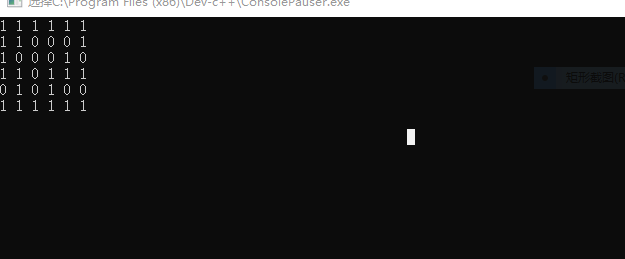
样例输入:
1 1 1 1 1 1
1 1 0 0 0 1
1 0 0 0 1 0
1 1 0 1 1 1
0 1 0 1 0 0
1 1 1 1 1 1
样例输出:
8
我输出之后就这样没反应,是我代码的问题吗?哪个大佬们看一下
# 太难了
# 链表忘了,又回去复习了一下
# 代码很糟糕
- #include<stdio.h>
- #include<malloc.h>
- #define N 6
- typedef struct ZERO //标记不被包围 0 的位置
- {
- int count;
- int x;
- int y;
- struct ZERO *next;
- } *ZEROP;
- int adjacent_to_zero(ZEROP head, ZEROP point); //检查是否与不被包围 0 相邻
- void print_struct(ZEROP, char*);
- ZEROP pop(ZEROP*, int n, int*);
- int main(void)
- {
- int arr[N][N] = { 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
- 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1,
- 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0,
- 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1,
- 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0,
- 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1};
-
- int i = 0;
- int j = 0;
- int count = 0;
- char un_zero_str[20] = "被包围 0";
- char zero_str[20] = "不被包围 0";
- ZEROP head, pn, pend; // head 不被包围 0 的位置头指针
- ZEROP un_head, un_pn, un_pend; // un_head 未知不被包围 0 的位置头指针
- ZEROP temp = NULL;
- for (i=0; i<N; i++) // 查找最外层有没有 0
- {
- for (j=0; j<N; j++)
- {
- if (i == 0 || i == N-1 || j == 0 || j == N-1)
- {
- if (!arr[i][j])
- {
- if (count == 0)
- {
- head = malloc(sizeof(struct ZERO));
- head->x = i;
- head->y = j;
- head->next = NULL;
- pn = pend = head;
- count++;
- head->count = count;
- }
- else
- {
- count++;
- pend = malloc(sizeof(struct ZERO));
- pn->next = pend;
- pend->count = count;
- pend->x = i;
- pend->y = j;
- pend->next = NULL;
- pn = pend; //标记 1
-
- }
-
- }
- continue;
- }
- }
- }
- int find = 2;
- if (!count) // 最外层没有 0 里面所有0都是被包围的0
- {
- find = 0;
- }
- int mark = 0;
- int un_count = 0;
- for (i=1; i<N-1; i++)
- {
- for (j=1; j<N-1; j++)
- {
- if (arr[i][j]) continue;
- temp = malloc(sizeof(struct ZERO));
- temp->x = i;
- temp->y = j;
- temp->next = NULL;
- if (!find) // 最外层没有 0
- {
- if (count == 0)
- {
- head = temp;
- head->next = NULL;
- pn = pend = head;
- count++;
- head->count = count;
- continue;
- }
- else
- {
- count++;
- pn->next = temp;
- temp->count = count;
- pn = temp; //标记 1
-
- }
- }
- else if (adjacent_to_zero(head, temp)) // 最外层有 0
- {
- un_count++;
- if (!mark)
- {
- un_head = temp;
- un_head->count = un_count;
- un_pn = un_head;
- mark = 1;
- continue;
-
- }
- un_pn->next = temp;
- temp->count = un_count;
- un_pn = temp;
- }
- else
- {
- count ++;
- pn->next = temp; //接着标记 1
- temp->count = count;
- pn = temp;
- }
- }
- }
- if (!find) // 最外层没有 0 直接打印结果
- {
- print_struct(head, zero_str);
- return 0;
- }
- //print_struct(un_head, un_zero_str);
- temp = un_head;
- int one = 0;
- while (1)
- {
- one ++;
- if (! adjacent_to_zero(head, temp)) //将未知 0 转入不被包围的 0
- {
- count++;
- //转入后更新链表
- if (un_head->next)
- temp = pop(&un_head, temp->count, &find);
- else find = 0;
- //print_struct(head, zero_str);
- //printf("count = %d\n", count);
- temp->count = count;
- pn->next = temp; //接着标记 1
- pn = temp;
- if (!find) break;
- if (find == 1)
- {
- temp = un_head;
- continue;
- }
- }
- //printf("one = %d\n", one);
- if (!temp->next) break;
- temp = temp->next;
- }
- //free(p);
- print_struct(head, zero_str);
- if (find)
- print_struct(un_head, un_zero_str);
- return 0;
- }
- int adjacent_to_zero(ZEROP head, ZEROP point)
- {
- while(1)
- {
- if (head->x == point->x) //同一行
- {
- if (head->y == point->y-1 || head->y == point->y+1)
- return 0;
- }
- if (head->y == point->y)
- {
- if (head->x == point->x+1 || head->x == point->x-1) //同一列
- return 0;
- }
- if (head->next == NULL) break;
- head = head->next;
- }
- return 1;
- }
- void print_struct(ZEROP head, char* title)
- {
- printf("%s:\n",title);
- while (1)
- {
- printf("COUNT = %d\tX = %d\tY = %d\n",head->count ,head->x+1 ,head->y+1);
- if (!head->next) break;
- head = head->next;
- }
- }
- ZEROP pop(ZEROP* linked_list, int n, int* find)
- {
- int count = 0;
- ZEROP result, previous;
- previous = result = *linked_list;
- while (1)
- {
- if (previous->count == n && count == 0)
- {
- *linked_list = previous->next;
- *find = 1;
- return previous;
- }
- else if (result->count == n)
- {
- previous->next = result->next;
- *find = 1;
- return result;
- }
- if (!result->next) break;
- previous = result;
- result = result->next;
- }
- *find = 2;
- return result;
- }
result:
- 不被包围 0:
- COUNT = 1 X = 3 Y = 6
- COUNT = 2 X = 5 Y = 1
- COUNT = 3 X = 5 Y = 6
- COUNT = 4 X = 5 Y = 5
- 被包围 0:
- COUNT = 1 X = 2 Y = 3
- COUNT = 2 X = 2 Y = 4
- COUNT = 3 X = 2 Y = 5
- COUNT = 4 X = 3 Y = 2
- COUNT = 5 X = 3 Y = 3
- COUNT = 6 X = 3 Y = 4
- COUNT = 7 X = 4 Y = 3
- COUNT = 8 X = 5 Y = 3
- --------------------------------
- Process exited after 0.01647 seconds with return value 0
- 请按任意键继续. . .
|
-
最佳答案
查看完整内容
# 太难了
# 链表忘了,又回去复习了一下
# 代码很糟糕
result:
|
 ( 粤ICP备18085999号-1 | 粤公网安备 44051102000585号)
( 粤ICP备18085999号-1 | 粤公网安备 44051102000585号)