|
|
15鱼币
from django.conf import settings
import hashlib
def md5(data_string):
obj = hashlib.md5(settings.SECRET_KEY.encode('utf-8'))
obj.update(data_string.encode('utf-8'))
return obj.hexdigest()
class a_user(forms.ModelForm):
passwords = forms.CharField(
label="确认密码",
widget=forms.PasswordInput(render_value=True)
)
class Meta:
model = models.admin
fields = ["username","password","passwords"]
widgets = {"password":forms.PasswordInput(render_value=True)}
def clean(self):
cleaned_data = super().clean()
pwd = md5(cleaned_data.get("password"))
pwds = md5(cleaned_data.get("passwords"))
print(pwd,pwds)
if pwds != pwd:
raise ValidationError("两次密码不一致,请重新输入")
else:
print(cleaned_data)
return cleaned_data
——————————————————————————
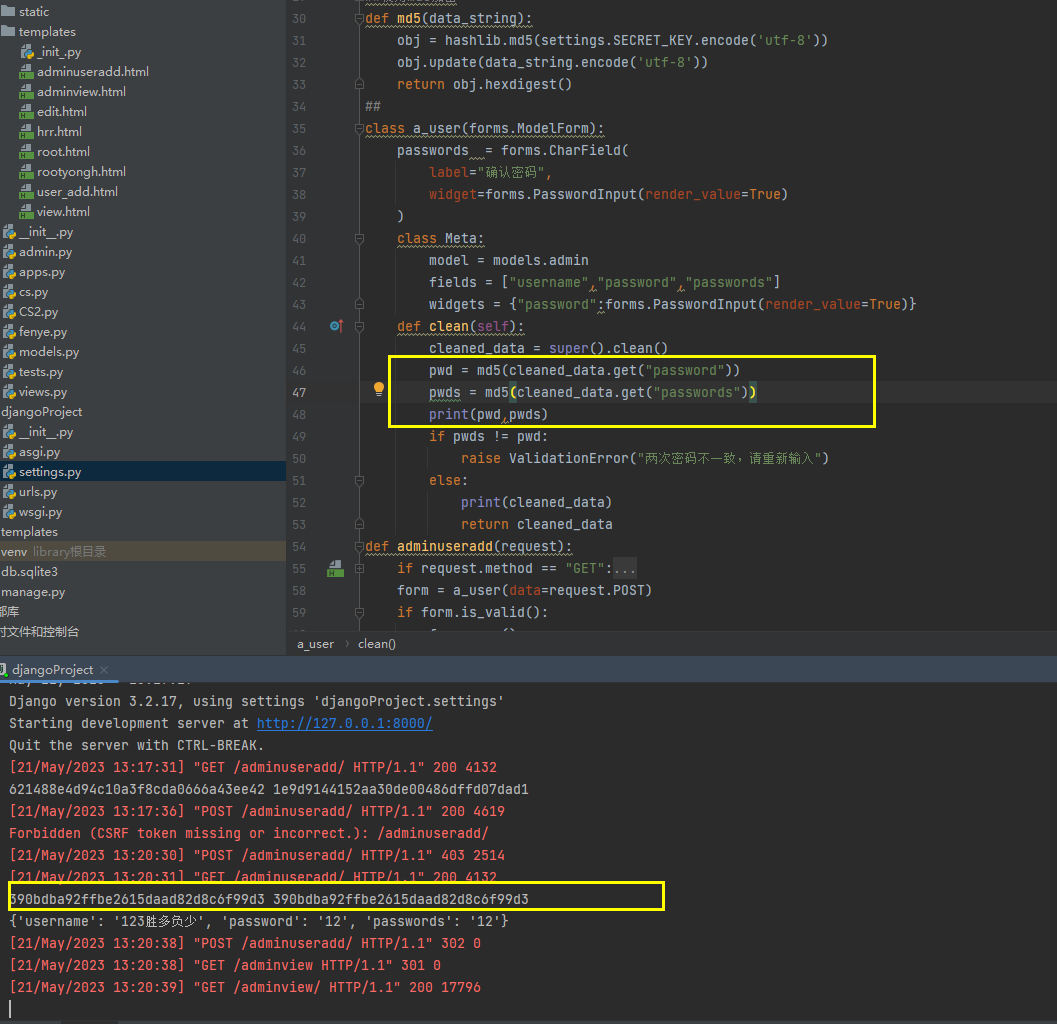
如上图所示 pwd pwds 两个字段可以正常转换MD5
return cleaned_data 这个数据还是原来的数据
且 print(md5(cleaned_data))
obj.update(data_string.encode('utf-8'))
AttributeError: 'dict' object has no attribute 'encode'有问题
怎么将 return cleaned_data 返回的数据变成md5数据
print(md5(cleaned_data)) 这个数据如果要这么写怎么写才正确
在你的代码中, cleaned_data 是一个字典类型的数据,而你的 md5 函数接收的是字符串。这就是为什么你在 md5(cleaned_data) 这段代码时会收到 AttributeError: 'dict' object has no attribute 'encode' 的错误信息,因为你尝试去编码一个字典类型的数据,而不是字符串。
关于如何将 cleaned_data 的返回数据变成md5数据,首先,你需要对字典里的每个值进行单独的md5编码。在此,你需要特别注意的是,你的密码应当在存储到数据库之前就已经被哈希过了。下面是如何修改你的 clean 函数以达到这个目的:
- def clean(self):
- cleaned_data = super().clean()
- pwd = md5(cleaned_data.get("password"))
- pwds = md5(cleaned_data.get("passwords"))
- print(pwd, pwds)
- if pwds != pwd:
- raise ValidationError("两次密码不一致,请重新输入")
- else:
- # 更新cleaned_data中的密码为哈希后的密码
- cleaned_data["password"] = pwd
- cleaned_data["passwords"] = pwds
- print(cleaned_data)
- return cleaned_data
此外,需要注意的是,你可能需要在保存你的 admin 模型对象之前更新密码字段,或者在保存模型之前修改密码的保存方式。最理想的方式是在模型层级处理密码的哈希,而不是在表单层级。例如,你可以使用Django的内置的 set_password 方法,它可以自动地将原始密码哈希化。为了安全起见,你可能不希望在任何地方都保留原始的密码。
不过如果你坚持要在表单层级处理密码的哈希,你可以选择在 save 方法中进行处理:
- class a_user(forms.ModelForm):
- # 省略其它代码...
- def save(self, commit=True):
- user = super().save(commit=False)
- password = self.cleaned_data.get("password")
- user.set_password(password) # 使用Django内置的set_password方法
- if commit:
- user.save()
- return user
以上代码展示了如何在保存用户时,将密码设置为其哈希值。其中 set_password 方法就是Django提供的一种安全的哈希密码的方式,你可以考虑使用它。
|
最佳答案
查看完整内容
在你的代码中, cleaned_data 是一个字典类型的数据,而你的 md5 函数接收的是字符串。这就是为什么你在 md5(cleaned_data) 这段代码时会收到 AttributeError: 'dict' object has no attribute 'encode' 的错误信息,因为你尝试去编码一个字典类型的数据,而不是字符串。
关于如何将 cleaned_data 的返回数据变成md5数据,首先,你需要对字典里的每个值进行单独的md5编码。在此,你需要特别注意的是,你的密码应当在存储到数据 ...
|
 ( 粤ICP备18085999号-1 | 粤公网安备 44051102000585号)
( 粤ICP备18085999号-1 | 粤公网安备 44051102000585号)