|
|
马上注册,结交更多好友,享用更多功能^_^
您需要 登录 才可以下载或查看,没有账号?立即注册
x
本帖最后由 andalousie 于 2014-3-25 22:51 编辑
原来写的《两种风格的Huffman树》增加了一个二进制流bitstream,用于一位位的读写,自己写的~
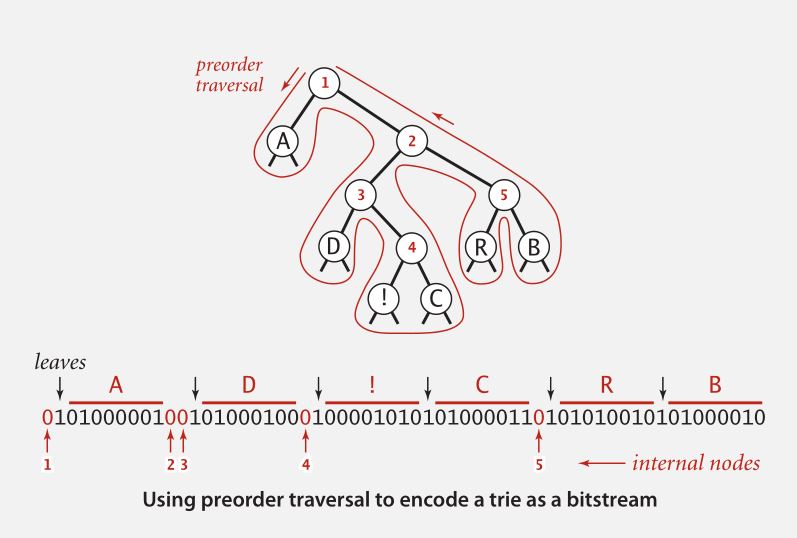
原理如图
- #if !defined BITSTREAM
- #define BITSTREAM
- //Alexander Misel 2014, Oschina
- //Open Source, free to copy
- #include <iostream>
- #include <fstream>
- #include <string>
- #include <cstdio>
- static const int READ_MODE = std::ios::in | std::ios::binary;
- static const int WRITE_MODE = std::ios::out | std::ios::binary;
- class bitostream
- {
- struct bit{
- bit() : _next(0) {};
- bit & operator=(unsigned char v)
- {
- _bit = v;
- return *this;
- }
- unsigned char _bit;
- bit * _next;
- };
- public:
- bitostream(std::string const & nameFile)
- : _stream(nameFile.c_str(), WRITE_MODE),
- _head(0), _byte(0), buffer(0), N(-1)
- {}
- //OUTPUT
- void allocate();
- void writeChar(unsigned char v);
- void writeBool(bool b);
- void bitout();
- private:
- std::ofstream _stream;
- bit * _head;
- bit * _byte;
- unsigned char buffer;
- int N;
- };
- inline void bitostream::allocate()
- {
- if(!_head)
- {
- bit * newByte = new bit;
- _head = newByte;
- _byte = newByte;
- * _byte = 0;
- buffer = 0;
- }
- else
- {
- _byte->_next = new bit;
- _byte = _byte->_next;
- * _byte = 0;
- buffer = 0;
- }
- }
- inline void bitostream::writeChar(unsigned char v)
- {
- if(N == -1 || N == 8)
- { allocate(); N=0; }
- if(!N)
- {
- N = 8;
- * _byte = v;
- return;
- }
- unsigned char tmp = v >> N;
- unsigned char pmt = v << (8-N);
- int save = N;
- buffer += tmp;
- N = 0;
- writeChar(buffer);
- N = -1;
- writeChar(pmt);
- buffer = pmt;
- N = save;
- }
- inline void bitostream::writeBool(bool b)
- {
- if(N == -1 || N == 8)
- { allocate(); N=0; }
- unsigned char tmp = b ? 1 : 0;
- tmp = tmp << (7-N);
- buffer += tmp;
- if(N == 7)
- {
- int save = N;
- N = 0;
- writeChar(buffer);
- N = save;
- }
- N++;
- }
- inline void bitostream::bitout()
- {
- bit * outByte = _head;
- while(outByte)
- {
- _stream.write(reinterpret_cast<char *>(outByte), 1);
- outByte = outByte->_next;
- }
- _head = 0;
- _byte = 0;
- buffer = 0;
- _stream.flush();
- }
- class bitistream
- {
- public:
- bitistream(std::string const & nameFile)
- : _stream(nameFile.c_str(), READ_MODE),
- inbuf(0), inN(0)
- {
- if(!_stream.is_open())
- throw "couldn't open file";
- pbuf = _stream.rdbuf();
- }
- //INPUT
- void get_in();
- bool isEmpty()
- {
- return (pbuf->sgetc() == EOF) && (inN == 8 || inN == 0);
- }
- unsigned char readChar();
- bool readBool();
- public:
- std::ifstream _stream;
- std::streambuf * pbuf;
- unsigned char inbuf;
- int inN;
- };
- inline void bitistream::get_in()
- {
- if(pbuf->sgetc() != EOF)
- inbuf = pbuf->sbumpc();
- }
- inline unsigned char bitistream::readChar()
- {
- if(!inN || inN == 8)
- {
- get_in();
- inN = 0;
- return inbuf;
- }
- unsigned char tmp = inbuf << inN;
- inbuf = 0;
- get_in();
- unsigned char pmt = inbuf >> (8-inN);
- tmp += pmt;
- return tmp;
- }
- inline bool bitistream::readBool()
- {
- if(!inN || inN == 8)
- {
- get_in();
- inN = 0;
- }
- unsigned char tmp = inbuf << inN;
- inN++;
- return (tmp & 0x80)>0;
- }
- #endif
huffman.cpp- #include <iostream>
- #include <string>
- #include "GPQ.h"
- #include "bitstream.h"
- const int R = 256;
- class Huffman
- {
- class Node
- {
- public:
- const unsigned char _ch;
- const int _freq;
- Node *_left, *_right;
- Node(unsigned char ch, int freq, Node* left, Node* right)
- : _ch(ch), _freq(freq), _left(left), _right(right)
- {}
- bool isLeaf() { return !_left && !_right; }
- bool compareTo(Node *that) { return _freq > that->_freq; }
- };
- struct buf
- {
- buf(): _id(-1) {}
- int index() { _id++; return _id; }
- int _id;
- }id;
- public:
- void expand(bitistream& trie, std::string& s, int N)
- {
- id._id = -1;
- Node *root = readTrie(trie);
- id._id = -1;
- for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
- {
- Node *x = root;
- while (!(x->isLeaf()))
- {
- if(s[id.index()] == '0')
- x = x->_left;
- else x = x->_right;
- }
- std::cout << x->_ch;
- }
- }
- void writeTrie(Node* x, bitostream& b)
- {
- if(x->isLeaf())
- {
- b.writeBool(true);
- b.writeChar(x->_ch);
- return;
- }
- b.writeBool(false);
- writeTrie(x->_left, b);
- writeTrie(x->_right, b);
- }
- Node* readTrie(bitistream& trie)
- {
- if(trie.readBool())
- {
- unsigned char c = trie.readChar();
- Node *fresh = new Node(c, 0, 0, 0);
- return fresh;
- }
- Node *x = readTrie(trie);
- Node *y = readTrie(trie);
- Node *fresh = new Node('\0', 0, x, y);
- return fresh;
- }
- void compress(std::string& s, bitostream& b)
- {
- // Tabulate frequency counts.
- int freq[R] = {0};
- for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); ++i)
- freq[s[i]]++;
- // Build Huffman code trie.
- Node *root = buildTrie(freq);
- std::string *st = new std::string [R];
- buildCode(st, root, "");
- // Print trie for decoder (recursive).
- writeTrie(root, b);
- // Use Huffman code to encode input.
- for (int id = 0; id < s.length(); id++)
- {
- std::string code = st[s[id]];
- std::cout << s[id] << " ";
- std::cout << code << std::endl;
- }
- }
- private:
- Node* buildTrie(int *freq)
- {
- GenericPQ<Node*> pq(R);
- for (int i = 0; i < R; i++)
- if (freq[i] > 0)
- pq.insert(new Node(i, freq[i], 0, 0));
- while (pq.size() > 1)
- {
- Node *x = pq.pop();
- Node *y = pq.pop();
- Node *parent = new Node('\0', x->_freq + y->_freq, x, y);
- pq.insert(parent);
- }
- return pq.pop();
- }
- std::string* buildCode(Node* root)
- {
- std::string *st = new std::string[R];
- buildCode(st, root, "");
- return st;
- }
- void buildCode(std::string *st, Node *x, std::string s)
- {
- if(x->isLeaf()) { st[x->_ch] = s; return; }
- buildCode(st, x->_left, s + '0');
- buildCode(st, x->_right, s + '1');
- }
- };
- int main()
- {
- Huffman code;
- std::string sample = "ABRACADABRA!";
- std::string coder = "0111110010110100011111001010";
- bitostream bin("huff.trie");
- code.compress(sample, bin);
- bin.bitout();
- bitistream by("huff.trie");
- code.expand(by, coder, 12);
- return 0;
- }
- 0,1,010000|00,0,0,1,010|00000,0,1,0|0100001,0|01000011|01,010100|00,1,01000|010.00000 wrong
- 0,1,010000|01,0,0,1,010|00100,0,1,0|0100001,0|01000011|01,010100|10,1,01000|010.00000 almost
- 0,1,010000|01,0,0,1,010|00100,0,1,0|0100001,1|01000011|01,010100|10,1,01000|010.00000 right
|
|
 ( 粤ICP备18085999号-1 | 粤公网安备 44051102000585号)
( 粤ICP备18085999号-1 | 粤公网安备 44051102000585号)