|
|
马上注册,结交更多好友,享用更多功能^_^
您需要 登录 才可以下载或查看,没有账号?立即注册
x
在这段代码中,我试图建立一个数学模型:平面上A、B两个无人机站分别位于半径为500 m的障碍圆两边直径的延长线上,A站距离圆心1 km,B站距离圆心3.5 km。两架无人机分别从A、B两站同时出发,以恒定速率10 m/s飞向B站和A站执行任务。飞行过程中两架无人机必须避开障碍圆、并且不得碰面 (即两架无人机的连线必须保持与障碍圆处于相交状态)要求两架无人机中第一个到达目的站点的用时最少,给出两架无人机的飞行航迹方案。 使用了模拟退火算法来进行优化 但是经过调参 输出结果要么是通过圆心的一条直线 要么是输出无法找到飞行轨迹 求助代码什么地方出了问题?
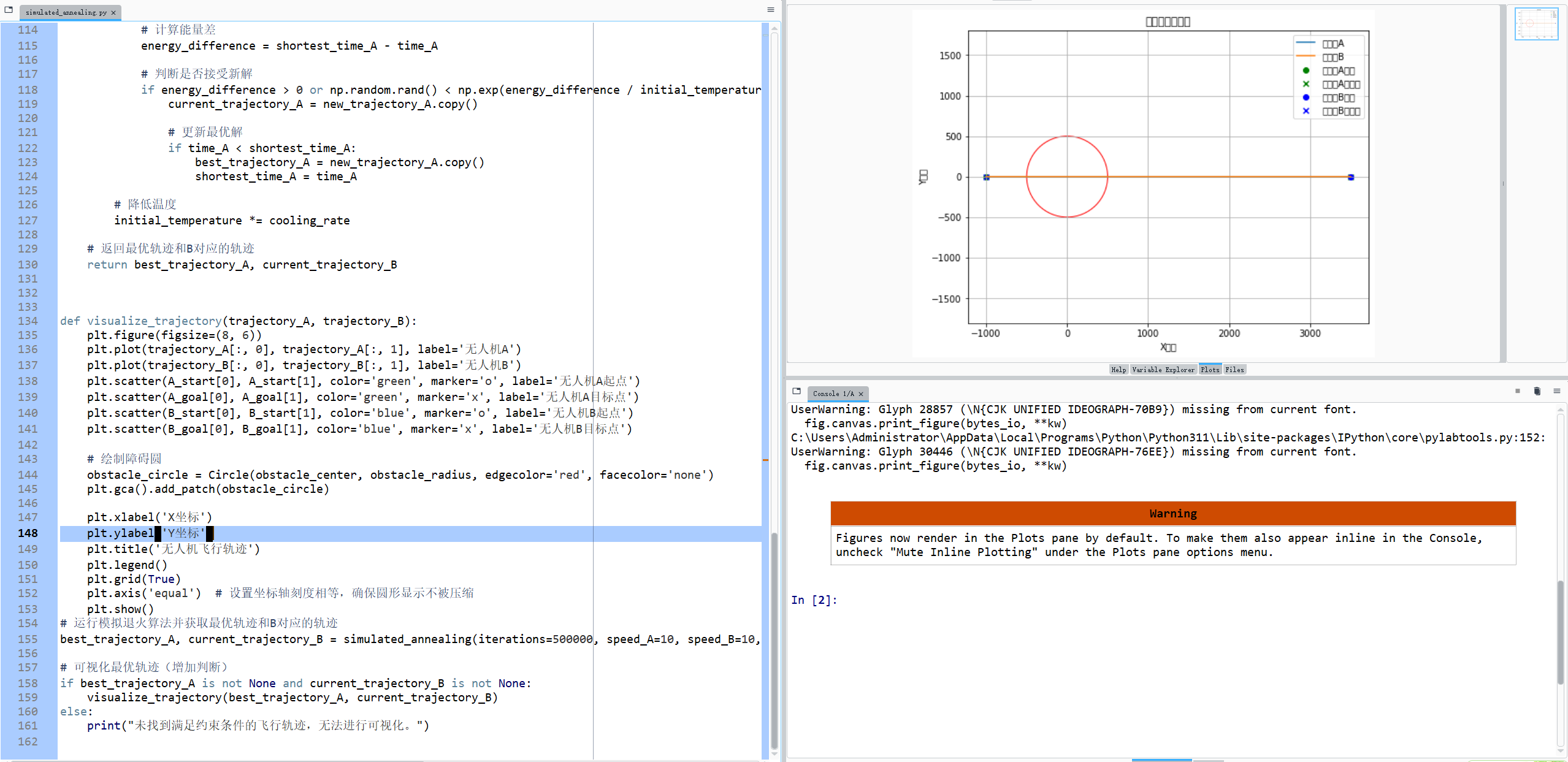
- import numpy as np
- import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
- from matplotlib.patches import Circle
- import tensorflow as tf
- from tqdm import tqdm
- # Example usage of simulated_annealing() function
- # Set initial temperature and cooling rate
- initial_temperature = 1000
- cooling_rate = 0.99
- # 障碍圆的位置和半径
- obstacle_center = np.array([0, 0])
- obstacle_radius = 500
- min_turning_radius = 30
- #无人机的速度 speed_A=10 speed_B=10
- # 两架无人机的初始位置和目标位置
- A_start = np.array([-1000, 0])
- A_goal = np.array([3500,0 ])
- B_start = np.array([3500, 0])
- B_goal = np.array([-1000, 0])
- def create_model(input_shape):
- model = tf.keras.Sequential([
- tf.keras.layers.Dense(512, activation='relu', input_shape=input_shape),
- tf.keras.layers.Dense(512, activation='relu'),
- tf.keras.layers.Dense(2) # 输出轨迹的点坐标
- ])
- return model
- # 生成随机飞行轨迹
- def generate_random_trajectory(start, goal, steps):
- x = np.linspace(start[0], goal[0], steps)
- y = np.linspace(start[1], goal[1], steps)
- trajectory = np.column_stack((x, y))
- return trajectory
- # 检查是否避开障碍圆
- def check_obstacle_avoidance(trajectory):
- distances = np.linalg.norm(trajectory - obstacle_center, axis=1)
- return np.all(distances > obstacle_radius)
- def check_minimum_turning_radius(trajectory, min_turning_radius):
- for i in range(len(trajectory) - 2):
- point1, point2, point3 = trajectory[i], trajectory[i+1], trajectory[i+2]
- # 计算转弯半径
- radius = np.linalg.norm(point2 - point1) / (2 * np.sin(np.arccos(np.dot((point2 - point1) / np.linalg.norm(point2 - point1), (point3 - point1) / np.linalg.norm(point3 - point1)))))
- if radius < min_turning_radius:
- return False
- return True
- # 计算直线到点的距离
- def line_point_distance(line_start, line_end, point):
- line_vec = line_end - line_start
- point_vec = point - line_start
- line_length = np.linalg.norm(line_vec)
- line_unit_vec = line_vec / line_length
- projection_length = np.dot(point_vec, line_unit_vec)
- if projection_length < 0:
- return np.linalg.norm(point_vec)
- elif projection_length > line_length:
- return np.linalg.norm(point - line_end)
- else:
- projection_point = line_start + projection_length * line_unit_vec
- return np.linalg.norm(point - projection_point)
- # 检查是否避免碰面
- def check_no_collisions(trajectory_A, trajectory_B):
- for i in range(len(trajectory_A) - 1):
- point_A1, point_A2 = trajectory_A[i], trajectory_A[i + 1]
- point_B1, point_B2 = trajectory_B[i], trajectory_B[i + 1]
- # 判断连线与障碍圆是否相交
- distance_A1 = line_point_distance(point_A1, point_A2, obstacle_center)
- distance_B1 = line_point_distance(point_B1, point_B2, obstacle_center)
- if distance_A1 <= obstacle_radius or distance_B1 <= obstacle_radius:
- return True
- return False
- #计算飞行时间
- def time_to_reach_goal(trajectory, speed):
- total_distance = 0.0
- for i in range(len(trajectory) - 1):
- total_distance += np.linalg.norm(trajectory[i + 1] - trajectory[i])
- time_to_reach_goal = total_distance / speed
- return time_to_reach_goal
- #模拟退火算法
- def simulated_annealing(iterations, speed_A, speed_B, initial_temperature, cooling_rate):
- current_trajectory_A = generate_random_trajectory(A_start, A_goal, steps=10000)
- current_trajectory_B = generate_random_trajectory(B_start, B_goal, steps=10000)
- best_trajectory_A = current_trajectory_A.copy()
- best_trajectory_B = current_trajectory_B.copy()
- shortest_time_A = time_to_reach_goal(current_trajectory_A, speed_A)
- for i in tqdm(range(iterations)):
- # 生成邻域内的随机新解
- new_trajectory_A = generate_random_trajectory(A_start, A_goal, steps=10000)
- new_trajectory_B = generate_random_trajectory(B_start, B_goal, steps=10000)
- # 检查约束条件
- if check_obstacle_avoidance(new_trajectory_A) and \
- check_no_collisions(new_trajectory_A, new_trajectory_B) and \
- check_minimum_turning_radius(new_trajectory_A, min_turning_radius):
- # 计算用时
- time_A = time_to_reach_goal(new_trajectory_A, speed_A)
- # 计算能量差
- energy_difference = shortest_time_A - time_A
- # 判断是否接受新解
- if energy_difference > 0 or np.random.rand() < np.exp(energy_difference / initial_temperature):
- current_trajectory_A = new_trajectory_A.copy()
- # 更新最优解
- if time_A < shortest_time_A:
- best_trajectory_A = new_trajectory_A.copy()
- shortest_time_A = time_A
- # 降低温度
- initial_temperature *= cooling_rate
- # 返回最优轨迹和B对应的轨迹
- return best_trajectory_A, current_trajectory_B
- def visualize_trajectory(trajectory_A, trajectory_B):
- plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6))
- plt.plot(trajectory_A[:, 0], trajectory_A[:, 1], label='无人机A')
- plt.plot(trajectory_B[:, 0], trajectory_B[:, 1], label='无人机B')
- plt.scatter(A_start[0], A_start[1], color='green', marker='o', label='无人机A起点')
- plt.scatter(A_goal[0], A_goal[1], color='green', marker='x', label='无人机A目标点')
- plt.scatter(B_start[0], B_start[1], color='blue', marker='o', label='无人机B起点')
- plt.scatter(B_goal[0], B_goal[1], color='blue', marker='x', label='无人机B目标点')
-
- # 绘制障碍圆
- obstacle_circle = Circle(obstacle_center, obstacle_radius, edgecolor='red', facecolor='none')
- plt.gca().add_patch(obstacle_circle)
-
- plt.xlabel('X坐标')
- plt.ylabel('Y坐标')
- plt.title('无人机飞行轨迹')
- plt.legend()
- plt.grid(True)
- plt.axis('equal') # 设置坐标轴刻度相等,确保圆形显示不被压缩
- plt.show()
- # 运行模拟退火算法并获取最优轨迹和B对应的轨迹
- best_trajectory_A, current_trajectory_B = simulated_annealing(iterations=500000, speed_A=10, speed_B=10, initial_temperature=1000, cooling_rate=0.99)
- # 可视化最优轨迹(增加判断)
- if best_trajectory_A is not None and current_trajectory_B is not None:
- visualize_trajectory(best_trajectory_A, current_trajectory_B)
- else:
- print("未找到满足约束条件的飞行轨迹,无法进行可视化。")
|
|
 ( 粤ICP备18085999号-1 | 粤公网安备 44051102000585号)
( 粤ICP备18085999号-1 | 粤公网安备 44051102000585号)